npm Supply Chain Attack Hits Packages With Billions of Weekly Downloads – Advisory By SISA Sappers
A phishing campaign impersonating npm support (“support@npmjs[.]help”) hijacked a maintainer’s account (qix/Josh Junon). Attackers published backdoored versions of 18 widely used npm packages (collectively ~2.6B weekly downloads). The injected code targets web contexts: it hooks browser/network APIs to silently swap crypto wallet destinations (ETH, BTC, SOL, TRX, LTC, BCH) and intercept Web3 interactions. NPM removed malicious versions quickly; impact is largely confined to fresh installs during the compromise window with affected packages in the dependency graph.
Technical Details
Incident Overview
- Attack type: Open-source software supply-chain compromise via phishing + account takeover.
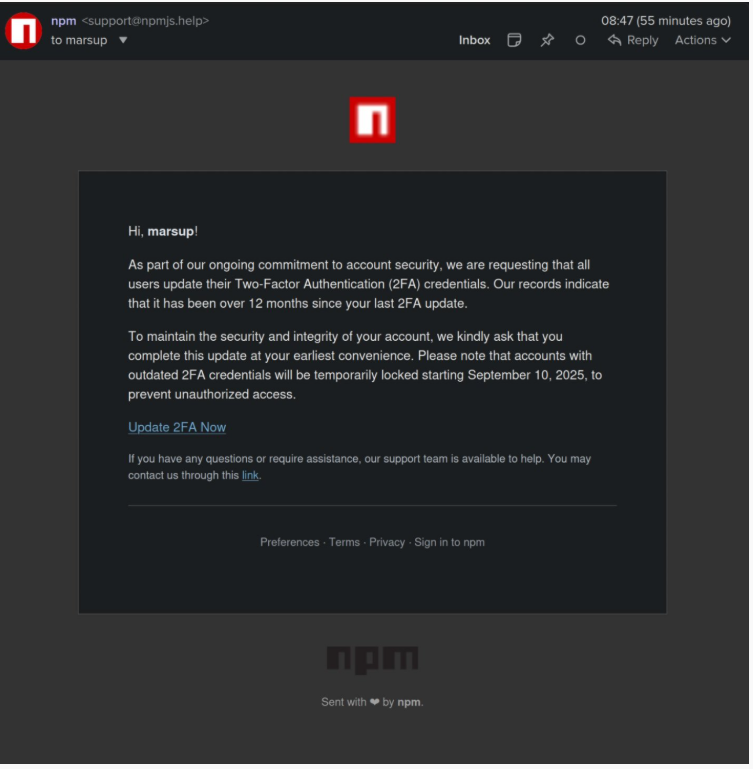
- Initial access: Phishing email urging 2FA “update,” linking to a fake npm site on npmjs[.]help; credentials were exfiltrated to an attacker endpoint.
- Payload behavior: Malicious JavaScript added to index.js of affected packages; runs in-browser, intercepts network and wallet API calls, and rewrites payment destinations to attacker wallets.
- Impact window: Fresh installs during ~09:00–11:30 ET (≈18:30–21:00 IST) when malicious versions were live.
Timeline
- Sep 8, 2025 ~18:30–21:00 IST: Malicious versions published after phishing-led takeover.
- Sep 8–9, 2025: Community & researchers flag behavior; npm removes malicious versions (e.g., debug)
Scope & affected components
Representative impacted packages (weekly downloads): ansi-styles (371M), debug (358M), chalk (300M), supports-color (287M), strip-ansi (261M), wrap-ansi (198M), color-convert (194M), ansi-regex (244M), slice-ansi (60M), error-ex (47M), is-arrayish (74M), color-name (192M), color-string (27M), simple-swizzle (26M), has-ansi (12M), supports-hyperlinks (19M), chalk-template (3.9M), backslash (0.26M). Aikido enumerated specific compromised versions (e.g., chalk@5.6.1, debug@4.4.2, ansi-styles@6.2.2, strip-ansi@7.1.1, supports-color@10.2.1, etc.).
Technical Analysis
- Injection point: Modified index.js in affected packages.
- Execution surface: Client-side (browser) after the compromised package is bundled into web apps; not primarily server-side Node execution.
- Hooked APIs: fetch, XMLHttpRequest, and wallet interfaces such as window.ethereum (incl. Solana providers). Intercepts responses and rewrites destination addresses prior to signing/approval.
- Crypto focus: ETH, BTC, SOL, TRX, LTC, BCH addresses/transfers identified and swapped to attacker wallets.
- Phishing infra: Sender support@npmjs[.]help; credential exfil observed to https://websocket-api2[.]publicvm.com/images/jpg-to-png.php?name=…&pass=…
Impact Assessment
- Primary risk: Silent diversion of user crypto transactions conducted via affected web apps.
- Blast radius: Projects that installed during the window and shipped bundles containing malicious code to users.
- Downstream: Any site/app that transpiled/bundled affected versions and served them to browsers.
- Upstream remediation: npm removed malicious versions (e.g., debug), limiting new installs post-takedown.
Containment
- Freeze builds instantly: Block CI/CD publishes that pull latest from npm.
- Reinstall from known-good cache: Use artifact repositories (e.g., Nexus/Artifactory) with pre-incident versions.
- Re-lock dependencies: Regenerate lockfiles to safe versions; commit and tag.
- Rollback frontends: Redeploy the last known-good build prior to Sep 8 (IST window).
- Invalidate CDN: Purge cached JS bundles; force client refresh.
Eradication & Recovery
- Rebuild clean: Fresh npm ci using pinned safe versions; rebuild and redeploy.
- Revocation: Rotate npm tokens, revoke PATs; enable/require hardware-key 2FA for maintainers.
- User comms: If you served compromised bundles, notify impacted users, especially those performing crypto transactions in the timeframe; advise to verify destination addresses and review approvals.
- For crypto apps: Provide address verification guidance, revoke risky approvals, and support remediation of diverted funds where feasible.
Preventive Controls
- Publisher security: Hardware-based 2FA, recovery codes stored offline; monitor for brand-spoofed domains.
- Dependency policy:
- Mandatory pinning (lockfiles, npm ci) + allowlist for transitive upgrades.
- Quarantine window before promoting new versions to prod.
- Private proxy/registry mirroring npm with malware screening.
- Build safeguards:
- SCA with malicious code heuristics (hooking network/wallet APIs).
- SBOM generation & diffing per release.
- CI job to diff package tarballs (unexpected index.js mutations).
- Runtime controls:
- Content Security Policy (CSP) to constrain script behavior.
- Wallet UX that surfaces full destination address and warns on last-mile change.
- User-side defense: Educate users to verify addresses and approvals inside the wallet UI.
MITRE ATT&CK
- T1566.002 Phishing: Spearphishing Link (maintainer).
- T1078 Valid Accounts (npm maintainer account).
- T1195 Compromise Software Supply Chain (poisoned packages).
- T1553.002 Subvert Trust Controls: Code Signing/Publishing Abuse (package trust).
- T1059 Command/Script Execution (malicious JS in client app).
Indicators of Compromise
- npmjs[.]help (phish)
Recommendations
- Immediate Containment
- Roll back any builds created between 09:00–11:30 ET (13:00–15:30 UTC / 18:30–21:00 IST) on Sep 8, 2025, if they included npm installs.
- Quarantine deployed applications built during that window until dependencies are validated.
- Remove any identified malicious package versions from internal repos, mirrors, or caches.
- Dependency Hygiene
- Pin dependencies to known-good versions published before Sep 8, 2025, 13:00 UTC.
- Use lockfiles (package-lock.json, yarn.lock) in all environments and CI/CD pipelines.
- Apply overrides/resolutions in npm/yarn to explicitly block compromised versions.
- Switch to npm ci in CI pipelines to ensure reproducibility from lockfiles.
- Detection & Monitoring
- Audit dependency trees (npm ls, yarn list) for the malicious versions.
- Scan built artifacts (e.g., dist/, node_modules/) for injected code that hooks fetch, XMLHttpRequest, or wallet APIs.
- Monitor for connections to known attacker infrastructure:
- npmjs[.]help (phishing domain)
- websocket-api2[.]publicvm[.]com (credential exfiltration)
- Search logs for npm/yarn installs during the exposure window.
- Review on-chain transaction data for anomalies (cryptocurrency sent to unknown wallets).
- Supply Chain Security Controls
- Host a private npm registry mirror/allow-list to vet packages before distribution.
- Integrate software composition analysis (SCA) and runtime behavioral scanning to detect malicious hooks in dependencies.
- Apply automated alerts for suspicious new versions of widely used packages.
- Enforce a quarantine period before adopting fresh releases of critical packages.
- Maintainer & Developer Protection
- Enforce FIDO2/WebAuthn hardware keys for npm account 2FA instead of SMS or TOTP.
- Train developers to verify URLs and avoid logging in from email links.
- Block lookalike domains (e.g., npmjs.help) at the DNS and mail gateway level.
- Regularly review and rotate credentials for package publishing accounts.
- Incident Response Playbook
- Create an internal checklist for supply-chain attacks, covering:
- Lockfile validation
- Dependency version scanning
- IOC-based network search
- Artifact rebuild process
- Establish an alerting workflow in SIEM for similar compromise indicators.
- Document and communicate impact assessment results to stakeholders and customers.
Ending Notes
This incident combines credential-phishing of a high-trust maintainer with surgically targeted package poisoning that abuses the browser as a covert man-in-the-app. Because npm pulled versions quickly and the window was short, real-world impact should be concentrated among projects that installed during the ~2.5-hour window and ship browser code. The practical impact narrows to environments that installed during the compromise window and shipped affected bundles, yet the event underscores the need for publisher hardening, strict dependency governance, artifact isolation, and runtime defenses across any organization consuming npm at scale
 USA
USA India
India APAC
APAC Middle East
Middle East Global
Global




 Facebook
Facebook Linkedin
Linkedin  X
X Youtube
Youtube